Publications
You can also check Google Scholar.
2025
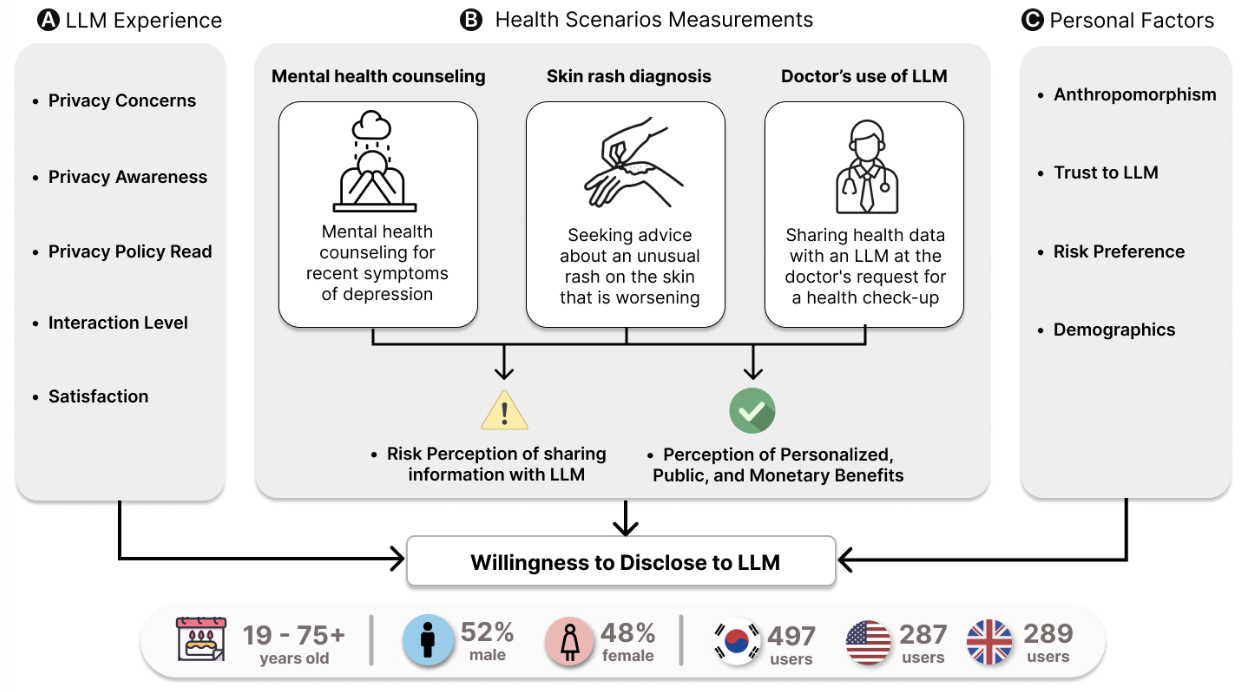 Privacy Disclosure to Large Language Models: A Large-Scale Study on Awareness, Benefits, and Concerns in Health Contexts Across Three CountriesYubin Choi, and other authorsPreprint, Under Revision & Resubimt for CHI 2025
Privacy Disclosure to Large Language Models: A Large-Scale Study on Awareness, Benefits, and Concerns in Health Contexts Across Three CountriesYubin Choi, and other authorsPreprint, Under Revision & Resubimt for CHI 2025Privacy has emerged as a critical societal concern in large language models (LLMs). Designing an effective and usable privacy experience for end-users requires more than technical mitigation; it necessitates a careful understanding and balancing of the risks and benefits perceived by the public. To identify public perceptions towards LLMs, we surveyed 1,073 individuals from the US, UK, and South Korea in three healthcare scenarios. The findings revealed that privacy concerns related to data leaks and disclosure without consent are major issues for end users. Across the studied countries, the potential for personalization and public benefits outweighed these concerns and positively influenced the willingness to disclose personal data. We found cross-cultural and individual differences in privacy perceptions, highlighting the need for culturally and personally tailored privacy designs. Given the limited privacy awareness among participants, we discuss opportunities for the responsible deployment of privacy-preserving LLMs and the associated legal implications.
 Leveling Up Together: Fostering Positive Growth and Safe Online Spaces for Teen Roblox DevelopersYubin Choi, Jeanne Choi, and Joseph SeeringPreprint, Under Revision & Resubimt for CHI 2025
Leveling Up Together: Fostering Positive Growth and Safe Online Spaces for Teen Roblox DevelopersYubin Choi, Jeanne Choi, and Joseph SeeringPreprint, Under Revision & Resubimt for CHI 2025Creating games together is both a playful and effective way to develop skills in computational thinking, collaboration, and more. However, game development can be challenging for younger developers who lack formal training. While teenage developers frequently turn to online communities for peer support, their experiences may vary. To better understand the benefits and challenges teens face within online developer communities, we conducted interviews with 18 teenagers who created games or elements in Roblox and received peer support from one or more online Roblox developer communities. Our findings show that developer communities provide teens with valuable resources for technical, social, and career growth. However, teenagers also struggle with inter-user conflicts and a lack of community structure, leading to difficulties in handling complex issues that may arise, such as financial scams. Based on these insights, we propose takeaways for creating positive and safe online spaces for teenage game creators.
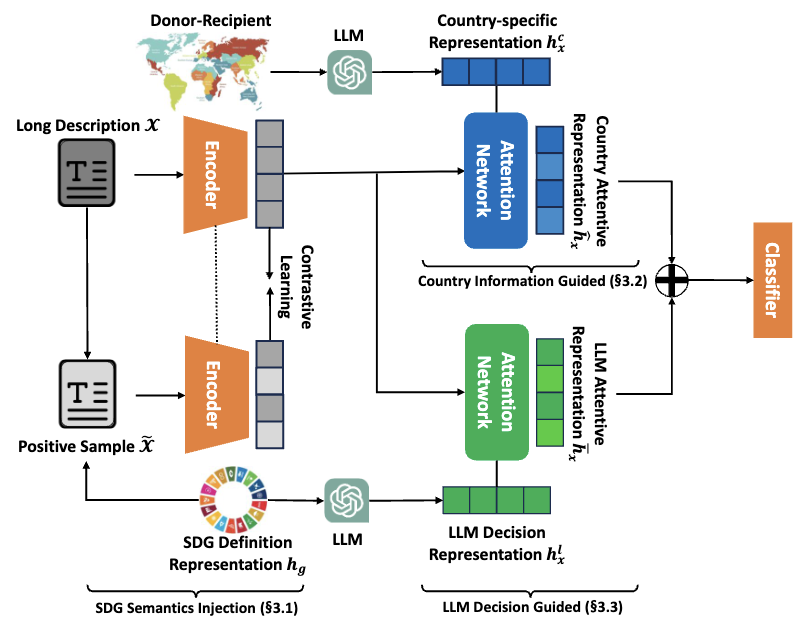 Multi-Label Classification of UN Sustainable Development Goals with Large Language ModelsYubin Choi (co-author), and other authorsPreprint, Submitted to WebConference (WWW) 2025
Multi-Label Classification of UN Sustainable Development Goals with Large Language ModelsYubin Choi (co-author), and other authorsPreprint, Submitted to WebConference (WWW) 2025International aid aimed at fostering economic growth and improving the welfare of developing countries is essential for achieving sustainable development. This study leverages an extensive dataset comprising over one million aid projects, capturing various attributes such as project descriptions, policy objectives, aid modalities, donor and recipient countries, and annual budgets. By mapping these projects to the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) using a multi-label classification approach, we propose an innovative AI model to alleviate the labor-intensive process of manual classification. Our approach demonstrates how integrating prior knowledge from large language models effectively addresses the complexities posed by the heterogeneous nature of development aid projects while respecting the specific contexts of each SDG. Validation confirms strong classification performance, with notable improvements in F1-score and AUROC compared to baseline models, further supported by human expert reviews in the domain of development cooperation. When applied to broader datasets, our model has the potential to uncover unseen trends in the temporal evolution of international development cooperation, stratified by the recipient country’s development status (e.g., low, middle, or upper-middle income). These insights offer valuable guidance to policymakers and non-governmental organizations, enabling more efficient project management and enhanced impact on sustainable development.
2024
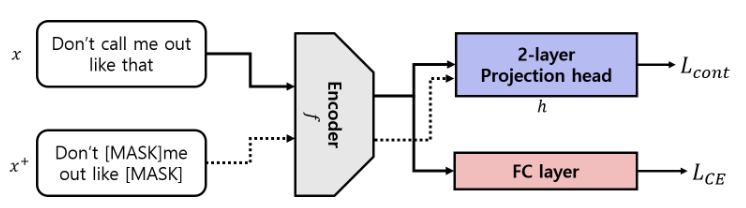 Detecting Offensive Language in an Open Chatbot PlatformHyeonho Song, Jisu Hong, Chani Jung, Hyojin Chin, Mingi Shin, Yubin Choi, Junghoi Choi, and Meeyoung ChaLREC 2024
Detecting Offensive Language in an Open Chatbot PlatformHyeonho Song, Jisu Hong, Chani Jung, Hyojin Chin, Mingi Shin, Yubin Choi, Junghoi Choi, and Meeyoung ChaLREC 2024While detecting offensive language in online spaces remains an important societal issue, there is still a significant gap in existing research and practial datasets specific to chatbots. Furthermore, many of the current efforts by service providers to automatically filter offensive language are vulnerable to users’ deliberate text manipulation tactics, such as misspelling words. In this study, we analyze offensive language patterns in real logs of 6,254,261 chat utterance pairs from the commercial chat service Simsimi, which cover a variety of conversation topics. Based on the observed patterns, we introduce a novel offensive language detection method—a contrastive learning model that embeds chat content with a random masking strategy. We show that this model outperforms existing models in detecting offensive language in open-domain chat conversations while also demonstrating robustness against users’ deliberate text manipulation tactics when using offensive language. We release our curated chatbot dataset to foster research on offensive language detection in open-domain conversations and share lessons learned from mitigating offensive language on a live platform.
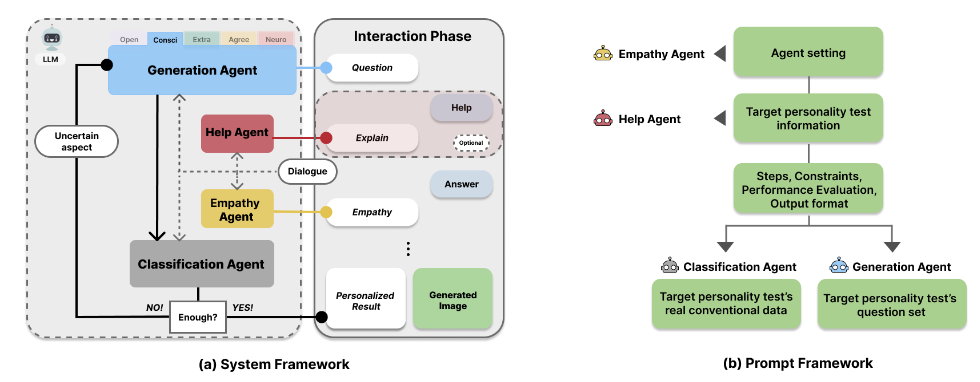 ChatFive: Enhancing User Experience in Likert Scale Personality Test through Interactive Conversation with LLM AgentsJungjae Lee*, Yubin Choi*, Minhyuk Song, and Sanghyun ParkCUI 2024
ChatFive: Enhancing User Experience in Likert Scale Personality Test through Interactive Conversation with LLM AgentsJungjae Lee*, Yubin Choi*, Minhyuk Song, and Sanghyun ParkCUI 2024Personality assessments provide insights into understanding individual differences. In HCI, personality assessments are used to model user behavior or tailor user interfaces. However, conventional Likert-scale personality tests face issues in user engagement and capturing comprehensive personality nuances. Building upon prior work using conversational user interfaces for personality prediction, we delve deeper into personalized personality tests. Through a formative study (n=4), we identified three design goals for user engagement. Informed by these goals, we propose a novel architecture integrating multiple large language model agents to support free-form conversation-based personality assessment. Our system, ChatFive, predicts users’ Big Five traits through real-time personalized dialogue. Evaluations from our user study (n=20) revealed that ChatFive significantly improved conveying true responses and felt more engaged, though requiring longer response times and different validation. We discuss the limitations on the validity of ChatFive and its implications.
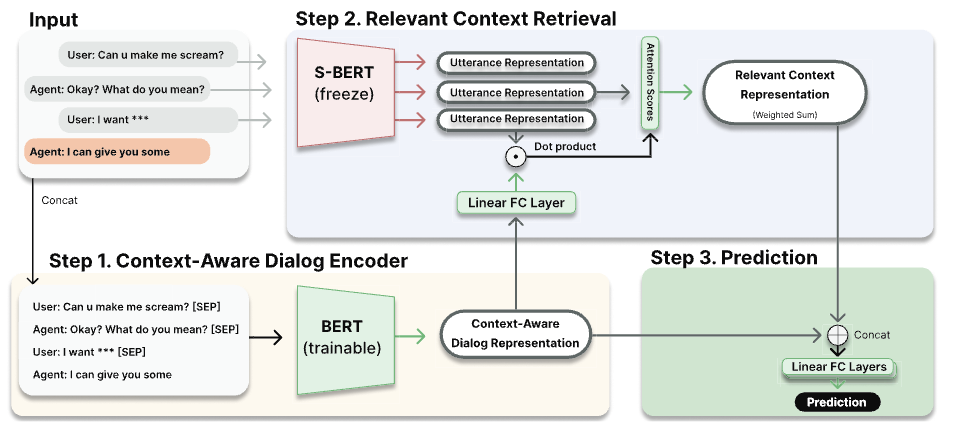 Context-Aware Offensive Language Detection in Human-Chatbot ConversationsMingi Shin, Hyojin Chin, Hyeonho Song, Yubin Choi, Junghoi Choi, and Meeyoung ChaBigComp 2024
Context-Aware Offensive Language Detection in Human-Chatbot ConversationsMingi Shin, Hyojin Chin, Hyeonho Song, Yubin Choi, Junghoi Choi, and Meeyoung ChaBigComp 2024Dialogs generated by chatbots may contain unethical and offensive language that can negatively affect users, the service, and society. Existing methods for automatically detecting offensive language are not effective for chat data, which is short and multi-turn and hence requires understanding the subtle context behind the language. We introduce a new offensive language dataset from real human-chatbot conversations with context-aware annotations that can identify the kinds of language that are offensive only in a certain context. We propose a neural network model CALIOPER (Context-Aware modeL for Identifying Offensive language using Pre-trained Encoder and Retrieval), which uses a context-aware encoder and attention mechanism to incorporate previous messages and retrieve relevant information for detecting implicit offensiveness. Experimental results show that the model performs well on multi-turn dialog data, par-ticularly for context-dependent offensive language. This work contributes to making a safer chatbot ecosystem by advancing techniques to detect offensive language in multi-turn dialog data. (Disclaimer: This work contains profanity due to the study topic, which we replace with * marks.)
2023
 Together we turn Uncertainty into Action: Understanding the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Supporting the Financial Concerns of Older AdultsYubin Choi, Dasom Choi, and Hwajung HongCSCW 2023 Companion
Together we turn Uncertainty into Action: Understanding the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Supporting the Financial Concerns of Older AdultsYubin Choi, Dasom Choi, and Hwajung HongCSCW 2023 CompanionArtificial Intelligence (AI) advancements have transformed digital banking by offering services such as personalized recommendations and interactive chatbots. However, only some AI systems target older adult users, given their relatively low usage of digital banking. Conversely, older adults may benefit the most from AI as handling finances becomes increasingly crucial after retirement. Our paper aims to fill this gap by 1) understanding the everyday financial concerns of older adults near retirement age and 2) exploring interests and needs in AI supporting their financial concerns. To understand the perspectives of older adults regarding the support of financial needs with AI, we conducted co-design workshops with 14 older adults. Our findings revealed three key concerns: retirement planning, grown children’s education and marriage expenses, and family healthcare costs. Also, participants were willing to use AI to glean the financial information they lacked and grow self-efficacy. Finally, we discuss the design opportunities of using AI to support older adults’ financial decisions.
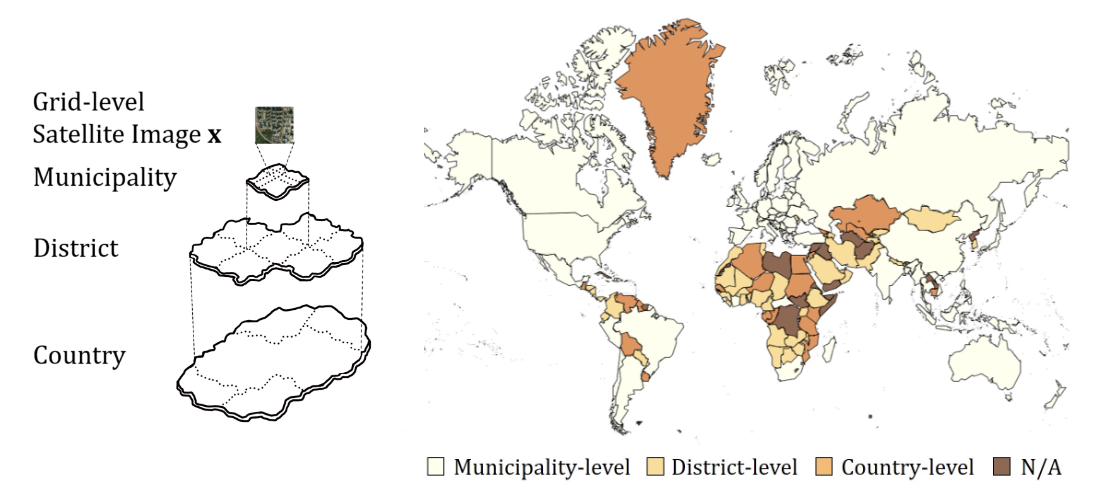 Fine-Grained Socioeconomic Prediction from Satellite Images with Distributional AdjustmentDonghyun Ahn, Minhyuk Song, Seungeon Lee, Yubin Choi, Jihee Kim, Sangyoon Park, Hyunjoo Yang, and Meeyoung ChaCIKM 2023 Short paper
Fine-Grained Socioeconomic Prediction from Satellite Images with Distributional AdjustmentDonghyun Ahn, Minhyuk Song, Seungeon Lee, Yubin Choi, Jihee Kim, Sangyoon Park, Hyunjoo Yang, and Meeyoung ChaCIKM 2023 Short paperWhile measuring socioeconomic indicators is critical for local governments to make informed policy decisions, such measurements are often unavailable at fine-grained levels like municipality. This study employs deep learning-based predictions from satellite images to close the gap. We propose a method that assigns a socioeconomic score to each satellite image by capturing the distributional behavior observed in larger areas based on the ground truth. We train an ordinal regression scoring model and adjust the scores to follow the common power law within and across regions. Evaluation based on official statistics in South Korea shows that our method outperforms previous models in predicting population and employment size at both the municipality and grid levels. Our method also demonstrates robust performance in districts with uneven development, suggesting its potential use in developing countries where reliable, fine-grained data is scarce.
2022
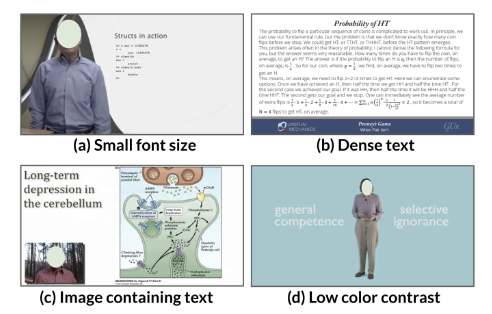 Mobile-Friendly Content Design for MOOCs: Challenges, Requirements, and Design OpportunitiesJeongyeon Kim, Yubin Choi, Meng Xia, and Juho KimCHI 2022
Mobile-Friendly Content Design for MOOCs: Challenges, Requirements, and Design OpportunitiesJeongyeon Kim, Yubin Choi, Meng Xia, and Juho KimCHI 2022Most video-based learning content is designed for desktops without considering mobile environments. We (1) investigate the gap between mobile learners’ challenges and video engineers’ considerations using mixed methods and (2) provide design guidelines for creating mobile-friendly MOOC videos. To uncover learners’ challenges, we conducted a survey (n=134) and interviews (n=21), and evaluated the mobile adequacy of current MOOCs by analyzing 41,722 video frames from 101 video lectures. Interview results revealed low readability and situationally-induced impairments as major challenges. The content analysis showed a low guideline compliance rate for key design factors. We then interviewed 11 video production engineers to investigate design factors they mainly consider. The engineers mainly focus on the size and amount of content while lacking consideration for color, complex images, and situationally-induced impairments. Finally, we present and validate guidelines for designing mobile-friendly MOOCs, such as providing adaptive and customizable visual design and context-aware accessibility support.
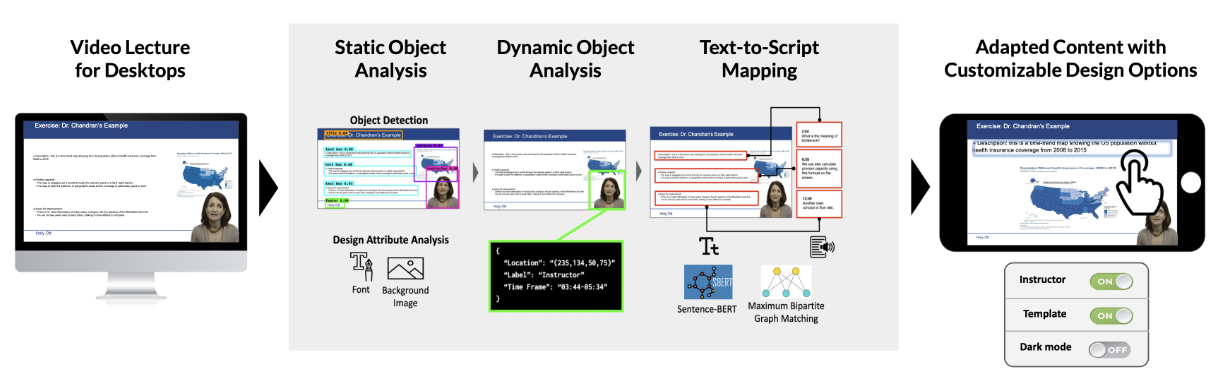 FitVid: Responsive and Flexible Video Content AdaptationJeongyeon Kim, Yubin Choi, Minsuk Kahng, and Juho KimCHI 2022
FitVid: Responsive and Flexible Video Content AdaptationJeongyeon Kim, Yubin Choi, Minsuk Kahng, and Juho KimCHI 2022Mobile video-based learning attracts many learners with its mobility and ease of access. However, most lectures are designed for desktops. Our formative study reveals mobile learners’ two major needs: more readable content and customizable video design. To support mobile-optimized learning, we present FitVid, a system that provides responsive and customizable video content. Our system consists of (1) an adaptation pipeline that reverse-engineers pixels to retrieve design elements (e.g., text, images) from videos, leveraging deep learning with a custom dataset, which powers (2) a UI that enables resizing, repositioning, and toggling in-video elements. The content adaptation improves the guideline compliance rate by 24% and 8% for word count and font size. The content evaluation study (n=198) shows that the adaptation significantly increases readability and user satisfaction. The user study (n=31) indicates that FitVid significantly improves learning experience, interactivity, and concentration. We discuss design implications for responsive and customizable video adaptation.